Useful Links
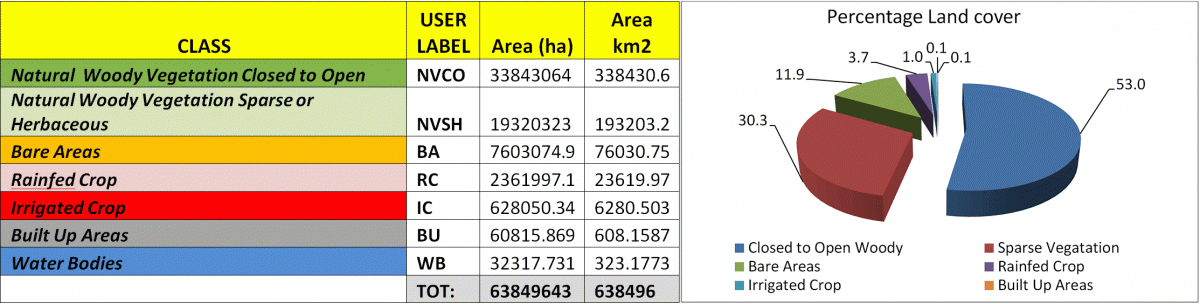
Land Cover
The vegetation in Somalia is varied and ranges from the forests of the Golis mountains in the North to the bush land in the Lag Badana ecosystem of the South. Patches of mangroves are found in Zeylac, Berbera and Calula on the northern coastline and in Kismayo on the southern coast - Methodology for Monitoring Mangroves - Report No L19. Expansive grasslands are found in Puntland and sparsely covered sand dunes cover a band of several kilometers along the coast.
Inappropriate land use has led to the original vegetation cover being heavily degraded, especially in northern Somalia, and in various places it has been entirely destroyed. This progressive destruction of plant life also has impaired animal habitats and reduced forage, affecting Somalia’s wildlife and its greatest food resource, its livestock (goats, sheep, camels, and cattle).
Mangroves in Somaliland The spatial distribution of vegetation in Somalia is as follows:
- The coastal plains vegetation consists mainly of herbaceous plants. The vegetation in this region extends to the feet and slopes of the Golis Mountains. Close to the mountains, the predominant vegetation is sparse bushy Acacia, Balanites aegyptiaca, and Commiphora associations including Boswellia species.
- In the hinterland plateaus, vegetation is dominated by open shrubs and woody plants of Acacia bussei, Acacia etbaica, Boscia spp, Cadaba spp, and Acacia mellifera. Some herbaceous plants (mainly Chrysopogon aucheri and Sporobolus spp.) can also be found here.
- In the northern Golis mountain range the vegetation consists of evergreen trees of Junperus procera and Juniperus excelsa and open shrubs of Buxus hilderbrandtii, Dodonea viscose and Terminalia brownii, etc. In the past, the Golis Forest remained largely uninhabited and protected while today it is experiencing increased exploitation pressure. There are now even human settlements in the forest.
- In the central plains, vegetation varies from extensive grassland along the fixed dune areas to shrubby bushland with scattered trees in the west toward the Ethiopian border. Plants and bushes include Andropoon kelleri, Chrysopogon aucheri, Soporobolus ruspolianus, Indigofera ruspolii, Acacia spp., Commiphora spp., Cordeauxia edulis, Delonix elata, Terminalia orbicularis and Dobera glabra etc.
- In the southern regions (especially in the floodplain), the vegetation type is mainly low deciduous bushland of Acacia spp. which extends to the coastal dunes.
- At certain points along the River Juba there are sections of riparian forest.
Mangrove swamp communities are also situated at the tidal estuaries of the seasonal rivers towards the Indian Ocean coast and Gulf of Aden. They areas include Bushbush, Caanoole and Lag Badanaa. The mangroves, like the Golis forest, are facing increased pressure of commercial exploitation.
A description of the main land cover types and vegetation units and their locations in two study areas is given in detail in the Land Cover of Selected Study Areas inSomaliland and Southern Somalia - Report No L-03.
The tree communities of forests, woodlands and mangrove swamps are facing increased pressure from commercial exploitation. Several studies at different scales have been carried out by SWALIM and are available in the publications library.


